Understanding the Education System in Vietnam: What is the Equivalent of High School?
Vietnam, a country located in Southeast Asia, has a rich cultural heritage and a rapidly growing economy. Like many countries, education plays a vital role in Vietnam’s development, and the country has a well-structured education system. However, the education system in Vietnam may be different from what we are familiar with in other countries. In this article, we will delve into the education system in Vietnam and explore what corresponds to high school in the United States or other Western countries.
Overview of the Education System in Vietnam
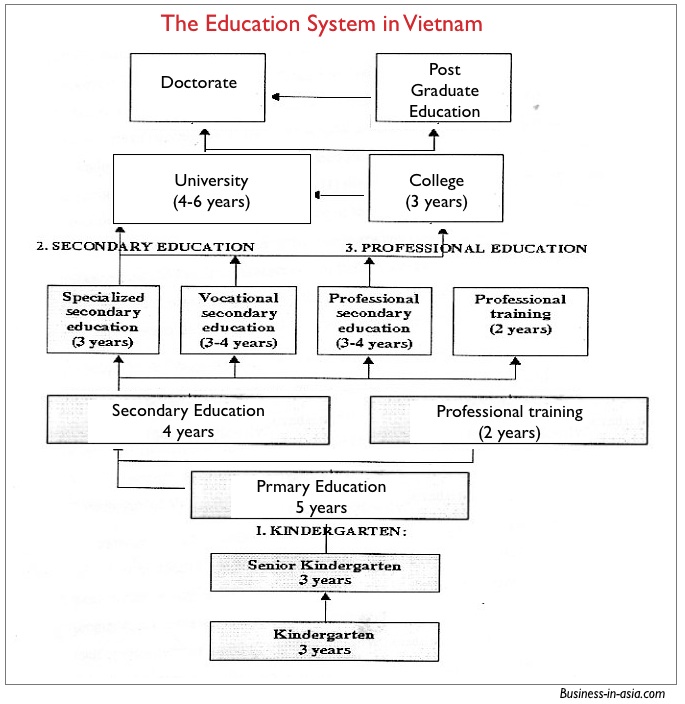
The education system in Vietnam is divided into several levels, including primary, lower secondary, upper secondary, and higher education. The education system is overseen by the Ministry of Education and Training (MOET), which is responsible for setting the curriculum, regulating schools, and evaluating student performance.
- Primary Education (Tiểu học): Primary education in Vietnam lasts for five years, from age 6 to age 11. This is the first stage of formal education, and students learn basic subjects such as Vietnamese language, mathematics, science, and social studies.
- Lower Secondary Education (Trung học cơ sở): Lower secondary education, also known as junior high school, lasts for four years, from age 11 to age 15. Students continue to study core subjects, including Vietnamese language, mathematics, science, and social studies, as well as foreign languages and physical education.
- Upper Secondary Education (Trung học phổ thông): Upper secondary education, also known as high school, lasts for three years, from age 15 to age 18. This is the final stage of secondary education, and students can choose to specialize in a particular field, such as mathematics, science, or humanities.
What is the Equivalent of High School in Vietnam?
In Vietnam, the equivalent of high school is upper secondary education, also known as Trung học phổ thông (THPT). THPT is a three-year program that prepares students for higher education or vocational training. Students typically take a variety of subjects, including:

- Compulsory subjects: Vietnamese language, mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, and physical education
- Elective subjects: foreign languages (English, French, German, etc.), information technology, economics, and social studies
- Specialized subjects: students can choose to specialize in a particular field, such as mathematics, science, or humanities
At the end of the three-year program, students take a national graduation examination, which is a requirement for graduation. The examination tests students’ knowledge and skills in core subjects, and the results are used to determine their eligibility for higher education.
Key Features of High School Education in Vietnam
Here are some key features of high school education in Vietnam:
- Curriculum: The curriculum is set by the MOET, and it is designed to prepare students for higher education or vocational training.
- Assessment: Students are assessed through regular exams and assignments, and the national graduation examination is a requirement for graduation.
- Teaching methods: Teaching methods in Vietnam are often traditional, with a focus on rote learning and memorization.
- Extracurricular activities: Extracurricular activities, such as sports, music, and drama, are not as prominent in Vietnam as they are in other countries.
- School life: School life in Vietnam is highly structured, with students typically attending school from 7:30 am to 5:00 pm, Monday to Saturday.

Challenges and Opportunities in Vietnam’s Education System
Despite its strengths, the education system in Vietnam faces several challenges, including:
- Overemphasis on rote learning: The education system in Vietnam is often criticized for its emphasis on rote learning and memorization, rather than critical thinking and problem-solving.
- Limited access to education: While education is compulsory in Vietnam, access to education is not universal, particularly in rural areas.
- Brain drain: Many of Vietnam’s brightest students choose to study abroad, which can lead to a brain drain and a shortage of skilled workers.
However, there are also opportunities for improvement and growth, such as:
- Increasing investment in education: The Vietnamese government has committed to increasing investment in education, which could lead to improvements in infrastructure and teacher training.
- Reforms to the curriculum: The MOET has introduced reforms to the curriculum, which aim to make education more relevant and effective.
- Growing demand for skilled workers: As Vietnam’s economy continues to grow, there is a growing demand for skilled workers, which could lead to more opportunities for graduates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the education system in Vietnam is well-structured, with a clear progression from primary to secondary education. The equivalent of high school in Vietnam is upper secondary education, also known as Trung học phổ thông, which lasts for three years and prepares students for higher education or vocational training. While the education system in Vietnam faces several challenges, there are also opportunities for improvement and growth, particularly with increasing investment in education and reforms to the curriculum.
